COBIT , ITIL , ISO 27001
COBIT
COBIT
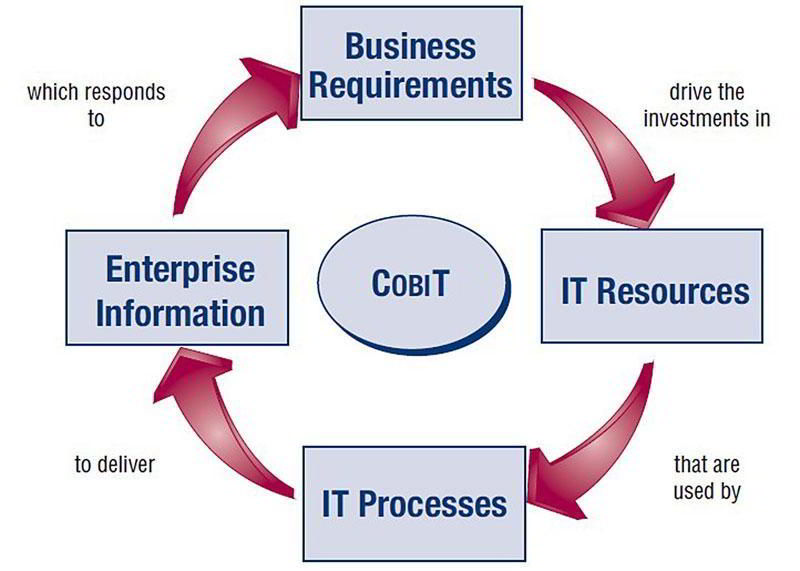
is stand for Control Objective over Information and Related Technology. Cobit
issued by ISACA (Information System Control Standard) a non profit organization
for IT Governance. The Cobit main function is to help the company, mapping
their IT process to ISACA best practices standard. Cobit usually choosen by the
company who performing information system audit, whether related to financial
audit or general IT audit.
COBIT
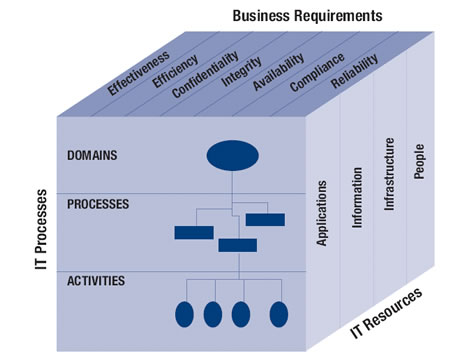
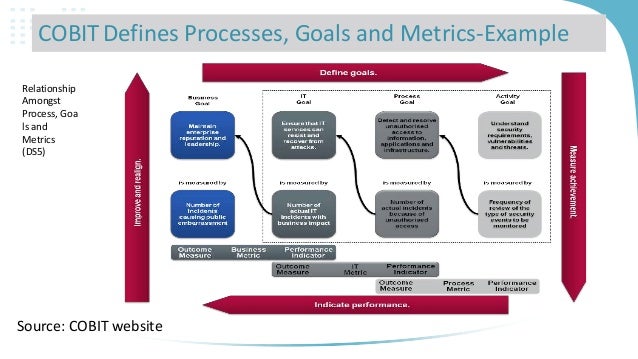
contains 34 IT processes, each with high-level control objectives (COs) and a
set of detailed control objectives (DCOs). In total, there is a sum of 318 DCOs
defined for these processes.
COBIT AND IT
COBIT®
provides guidance for executive management to govern IT within the
enterprise
•
More effective tools for IT to
support business goals
•
More transparent and
predictable full life-cycle IT costs
•
More timely and reliable
information from IT
•
Higher quality IT services and
more successful projects
•
More effective management of
IT-related risks
•
COBIT is often used at the highest level of IT
governance
•
It harmonises practices and standards such as
ITIL, ISO 27001 and 27002, and PMBOK
ITIL, ISO 27001 and 27002, and PMBOK
–
Improves their alignment
to business needs
to business needs
–
Covers full spectrum of
IT-related activities
IT-related activities
ITIL
The
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) framework is designed to
standardize the selection, planning, delivery and support of IT services to a
business. The goal is to improve efficiency and achieve predictable service
levels. The ITIL framework enables IT to be a business service partner, rather
than just back-end support. ITIL guidelines and best practices align IT actions and
expenses to business needs and change them as the business grows or shifts
direction.
The
benefits of adopting ITIL can offer users improved IT services, improved
customer satisfaction through a more professional approach to service delivery,
improved productivity, improved use of skills and experience and improved
delivery of third party services.
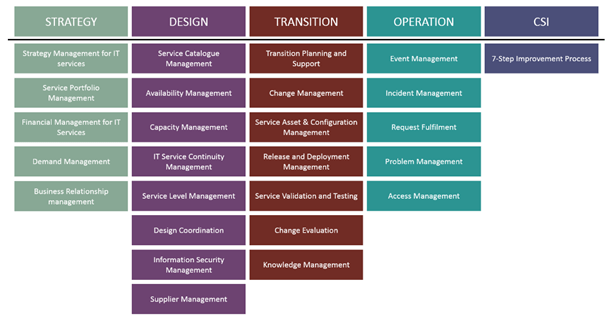
ITIL
2007 has five volumes, published in May 2007, and updated in July 2011 as ITIL
2011 for consistency:
1. ITIL Service Strategy: understands
organizational objectives and customer needs.
2. ITIL Service Design: turns the service
strategy into a plan for delivering the business objectives.
3. ITIL Service Transition: develops and
improves capabilities for introducing new services into supported environments.
4. ITIL Service Operation: manages services
in supported environments.
5. ITIL Continual Service
Improvement: achieves services incremental and large-scale improvements.

ISO
27001
The
ISO 27001 standard was published in October 2005. ISO 27001 was formerly called
BS7799-2 standard. It is the specification for an Information Security
Management System. It is the formal set of specifications against which
organizations may seek independent certification of their ISMS.
The objective of the ISO 27001 standard is to provide a model for establishing, implementing, operating, monitoring, reviewing, maintaining and improving an information security management system.
The objective of the ISO 27001 standard is to provide a model for establishing, implementing, operating, monitoring, reviewing, maintaining and improving an information security management system.
BENEFİTS
OF ISO 27001
Identify
risks and put controls in place to manage or eliminate them
Flexibility to adapt controls to all or selected areas of your business
Gain stakeholder and customer trust that their data is protected
Demonstrate compliance and gain status as preferred supplier
Meet more tender expectations by demonstrating compliance
Flexibility to adapt controls to all or selected areas of your business
Gain stakeholder and customer trust that their data is protected
Demonstrate compliance and gain status as preferred supplier
Meet more tender expectations by demonstrating compliance
ISO27001 is much more different between COBIT and
ITIL, because ISO27001 is a security standard, so it has smaller but deeper
domain compare to COBIT and ITIL.

COMPARISON
BETWEEN 3 STANDARTS
Strengths
·
COBIT
is managed by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) and
keeps the standard up-to-date and on-par with current technology. It is a
globally accepted standard and encompassed far more than just the information
security scope that other standards are limited to. Accordingly, it is also
easier to partially implement COBIT without requiring a full-spectrum analysis
and commitment by the organization.
·
ITIL
is created and managed by the U.K. government, and is a natural fit for
companies in that area of the world. However, the ITIL standard is used
worldwide and may be considered for any company regardless of geographical
location. ITIL excels at increasing visibility into and management of internal
process to positively impact efficiency and economy.
·
ISO
27002 is associated with a very respected and widely known standard (ISO
27001), and will be recognized and understood by those familiar with the
ISO/IEC standards. This standard allows system managers to identify and
mitigate gaps and overlaps in coverage.
·
The
level of detail afforded by implementing a framework based on NIST is
considerable, and an organization not wishing to spend time on customizing a
framework for their specific industry or nature may wish to use NIST assuming
that the level of detail is complimentary to its goals.
Weaknesses
·
While
being widely scoped is can be viewed as a strength for COBIT, it can also be a
detractor during implementation. Being by design not limited to a single area,
it can often lead to gaps in coverage.
·
While
focused on information security only, ITIL is considered to be a higher-level
standard than ISO 27002, and points to ISO standards for detailed
implementation. Specific implementation details are rather lacking.
·
ISO
27002 is focused specifically and purposefully on information security and is
therefore limited in scope compared to other standards such as COBIT.
·
Similar
to ISO 27002, NIST is limited in scope to information security, whereas COBIT
and ITIL are more general in nature. Multiple publications must be processed
and implemented in order to achieve compliance, which can lead to coverage
gaps.
When to Use
·
COBIT
is a good candidate when an organization wishes to create an organization-wide
framework for management that is scoped outside of information security only.
While not providing direct accreditation, certification can be achieved through
closely aligned paths.
·
ITIL
points to ISO standards as a framework in which to implement a solution. This
applies well for organizations wishing to use ISO standards with global recognition
without necessarily achieving an ISO 27001 certification.
·
The
associated certification for ISO 27002 (ISO 27001) provides a worldwide
recognition and acceptance, and therefore organizations wishing to operation
across international boundaries may find implementation and certification
advantageous. Additionally, some ISO 27001 certified companies require partners
to become certified as well.
·
U.S.
government organizations are required to use NIST in order to comply with
federal law. Additionally, non-federal organizations may also use the NIST
standard, but other standards such as ISO 27002 or ITIL may be better suited as
NIOST can be difficult to implement for some organizations.

What
is the easiest standard?
From the implementatation view, ITIL is the
easiest standard to be implemented. Because, ITIL could be implemented
partially and still not have impact on performance. Example, if IT departement
lack of budget and he could choose to implement IT Service Delivery layer only,
and the next year he will try to implement IT Release Management or IT Problem
Management.
However COBIT and ISO27001 is quite difficult
to be implemented partially, since it should see a process in bigger view first
before they could implemented partially.

REFERENCES
Guzel bir paylasim tesekkurler.
YanıtlaSil